| configs | ||
| files | ||
| images | ||
| rel-eng | ||
| scripts | ||
| dist-git.spec | ||
| install-dist-git.sh | ||
| README.md | ||
Dist Git
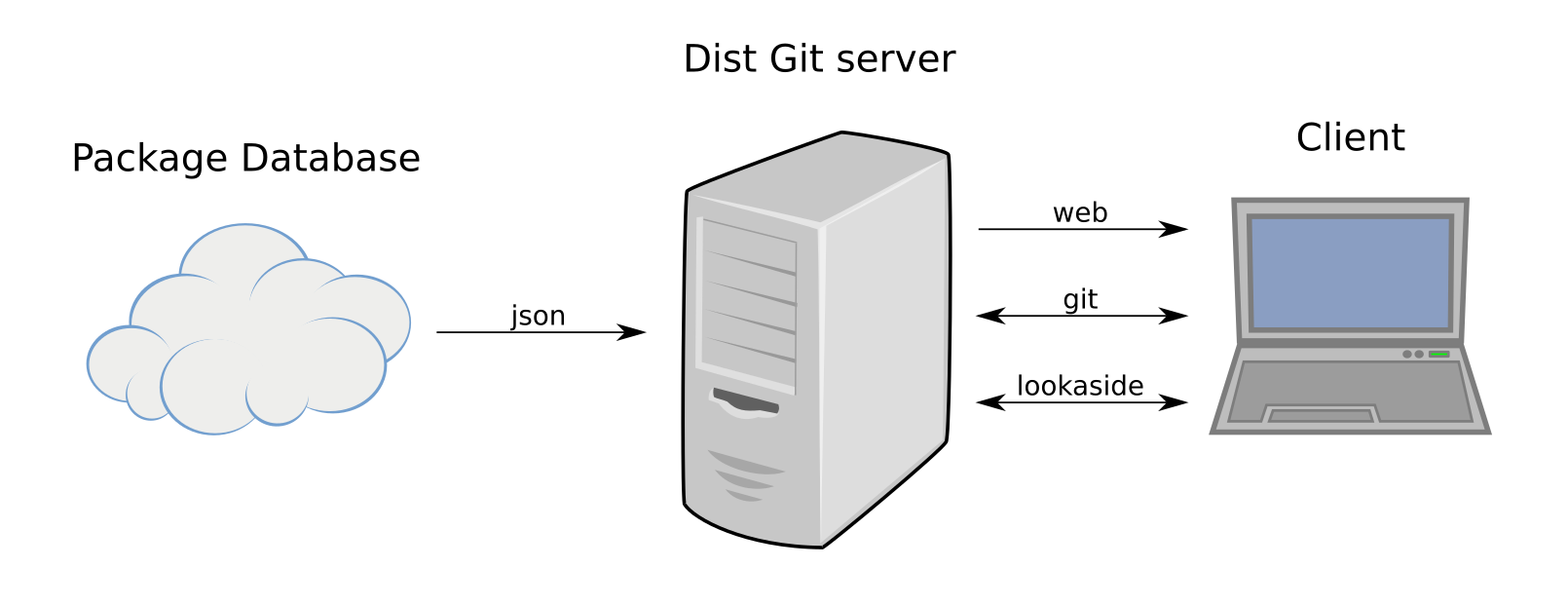
Dist Git is a remote Git repository specificaly designed to hold RPM package sources. It consists of three main modules:
- Git repository with permissions managed by Gitolite
- Lookaside cache to store source tarballs
- Scripts to manage
How does it work
The Dist Git server repeatedly asks a package database for information about packages. This information contains a list of packages and other information. Each package can have a list of users or groups entitled to commit to this package and a list of platforms for which the package is built. Sources for each platform are held in corresponding branches.
User cat interact with the Dist Git server using client probably based on rpkg. The client authenticates with an ssh certificate for git communication and with an http client certificate for uploads to the lookaside cache.
Package Database communication
The following is an example JSON data comming from the Package Database which would create two packages: copr-frontend and copr-backend. The first package would be for Fedora 21 only and permissions to commit into this repo would be granted to users mirek, adam and anyone in the group provenpackager. The copr-backend package would be for Fedora 21 and CentOS 7. The permissions would be processed the same way as for the first package.
"packageAcls": {
"copr-frontend": {
"fedora-21": {
"commit": {
"groups": ["provenpackager"],
"people": ["mirek", "adam"]
}
}
},
"copr-backend": {
"fedora-21": {
"commit": {
"groups": ["provenpackager"],
"people": ["mirek", "valentin"]
}
},
"centos-7": {
"commit": {
"groups": ["provenpackager"],
"people": ["mirek", "valentin"]
}
}
}
}
The final result would consist of two package repositories:
- copr-frontend with a single branch: fedora-21
- copr-backend with two branches: fedora-21 and centos-7
Client Authentication and Authorization
In order to make changes in the package repositories, client needs to have a permission to do that. Both Git and Lookaside Cache have their own auth process.
Git uses ssh communication and client authenticates with public key. Each user needs to have an account on the server and be in a packager group. Their ssh shell must be set to "HOME=/var/lib/dist-git /usr/share/gitolite3/gitolite-shell %(username)s" in order to have authorization working.
Authorization is done by Gitolte. The configuration file describing all the permisions is automaticaly generated each time a Package Database is queried. Gitolite uses system users and groups.
Lookaside Cache uses https communication and client authenticates with ssl client certificate. The Dist Git service provider needs to issue the client certificate for every user.
There is no authentication needed in order to read from the server.